Only because of the joint action of the skeleton and muscles of our body are we able to move and this. Osteon the functional unit of compact bone.

Osteon Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Course Title BIOL 2401.
. Structure and function Structure of the bone. Bones and cartilage are a part of the specialised connective tissue. What is an osteon.
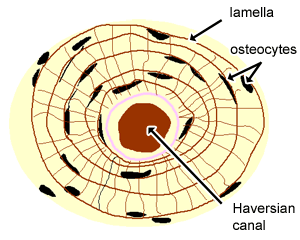
Osteons -the basic functional and structural unit of mature compact bone -cylinder running parallel to the long axis -aka Haversion systems Central Haversian canal central channel containing blood vessels nerves Lamellae weight-bearing column-like matrix tubes made up of mainly collagen -- tree-like rings Perforating Volkmann canal. An osteon is made up of the Haversian canal osteocyte and canliculi. Each osteon has a cylindrical structure that consists of the following components.
The central canal contains blood vessels lymphatic vessels lymphatic vessels and nerves. Name the structurefunctioncomponents of osteon. The combination of organic 30-40 and inorganic 60-70 substances is a feature of the.
Osteon is the structural unit of bone. The Concentric Lamellae surrounds the central canal and gives bone their strength. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae singular lamella.
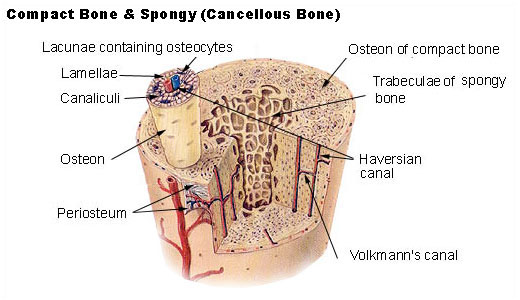
Only because of the joint action of the skeleton and muscles of our body we are able to move. Connect Plus 2 Semester Access Card for Principles of Anatomy and Physiology Includes APR PhILS Online Access 2nd Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 6 Problem 11Q. Osteon the chief structural unit of compact cortical bone consisting of concentric bone layers called lamellae which surround a long hollow passageway the Haversian canal named for Clopton Havers a 17th-century English physician.
Inside the cement line are concentric layers of bone lamellae made of. An osteon refers to a unit of compact bone that includes a central canal and the concentric layers of lamellae and osteocytes surrounding the canal. The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon or Haversian system.
Vessels are surrounded by 4-20 rings of lamellae. Each osteon consists of lamellae which are layers of compact matrix that surround a central canal called the Haversian canal. Each osteon is made up of concentric layers.
This central canal is referred to as the Haversian canal. The Haversian canal contains small blood vessels responsible for the blood supply to osteocytes individual. Calcium 8 Describe the structure of an osteon Compact bone is composed of.
Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain a mineral matrix and living osteocytes connected by canaliculi which transport blood. Although cortical bone provides the majority of mechanical strength for a bone there are few studies focusing on. The Haversian canal that is located in the center of the osteon.
It is further divided into two types that are fluid connective tissue and skeletal connective tissues. It is a passageway for blood vessels and nerves that supply the bone. Each group of concentric circles each tree makes up the microscopic structural unit of compact bone called an osteon this is also called a Haversian system.
Only because of the joint action of the skeleton and musclesour body we are able to move and. Blood comprises fluid connective tissue and we will learn about skeletal connective tissue. An osteon comprises a long hollow central canal that is surrounded by concentric layers called lamallae.
The osteon or haversian system həˈvɜːrʒən named for Clopton Havers is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone. An osteon is a long cylindrical unit that runs parallel to the diaphysis of the long bone. The hollow center of an osteon also known as a Haversian canal.
Osteon means bone and the process of formation of bone is known as osteogenesis. Structure and function Structure of the bone. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically between 025 mm and 035 mm in diameter.
The osteon consists of a central canal called the osteonic haversian canal which is surrounded by concentric rings lamellae of matrix. Osteon is the structural unit of bone. School San Jacinto College.
It components are as follows. Starting from the outside of the osteon and moving inward the osteon is rimmed by the cement line a band of less stiff material with an important role in resisting fracture 33. Pages 5 This preview shows page 2 - 4 out of 5 pages.
Between the rings of matrix the bone cells osteocytes are located in spaces called lacunae. The long axis of the osteon is parallel to the long axis of the bone. Their length is often hard to define but estimates vary from several millimeters to around 1 centimeter.
Bone is laid down around the central canal in concentric rings called lamellae. Calcium 8 describe the structure of an osteon compact. Osteocytes live in lacunae that are between each ring of lamella.
There are about 206 bones in the human body but few people know their structure and understand why they are. Each ring of the osteon is made of collagen and calcified matrix and is called a lamella plural lamellae. Blood vessels run throughout central canals in compact bone.
Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal or Haversian canal which contains blood vessels nerves and lymphatic vessels. The combination of organic 30-40 and inorganic 60-70 of substances is a feature of the. Describe the structure of compact bone.
Structure and function Content. Structure Turnover and Regeneration Abstract Bone is composed of dense and solid cortical bone and honeycomb-like trabecular bone. An osteon is a few millimeters in length and has a diameter of approximately 02 mm 31 32.
Osteon anatomy Britannica. They are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone.

Structure Of Bones Biology For Majors Ii

Cartilage Bone Ossification The Histology Guide
5 Structure Of The Osteons Of Cortical Bone Junqueira And Carneiro 1992 Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments